IDDSI & TEXTURE MODIFIED DIETS
Each year, individuals of all ages all around the world are diagnosed with feeding or swallowing difficulties (dysphagia). Put simply, dysphagia can be described as difficulty moving food, liquid, saliva or medication from the mouth to the stomach.
The consequences of dysphagia include dehydration, malnutrition, aspiration and asphyxiation and a negative impact on quality of life and social participation in eating and drinking.
It's currently estimated that ~ 590 million people around the world are living with dysphagia. Although dysphagia touches individuals across their life span, it is most prevalent at the end of life, with the elderly being most affected.
Although sufferers are sometimes unaware of the disorder, dysphagia is a highly prevalent clinical condition as it affects:
- > 30% of patients with stroke,
- 60–80% of patients with neurodegenerative diseases,
- 10–30 % of adults aged 65 and older
- > 51% of institutionalized elderly patients
Countries across the globe have moved towards standardising the terminology and definitions used to describe texture-modified foods and liquids, this is known as the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) framework.
The IDDSI framework consists of a continuum of 8 levels (0 - 7), where drinks are measured from Levels 0 – 4, while foods are measured from Levels 3 – 7. The IDDSI Framework provides a common terminology to describe food textures and drink thickness.
IDDSI Testing Methods are intended to confirm the flow or textural characteristics of a particular product at the time of testing. Testing should be done on foods and drinks under the intended serving conditions (especially temperature).The clinician has the responsibility to make recommendations for foods or drinks for a particular patient based on their comprehensive clinical assessment.
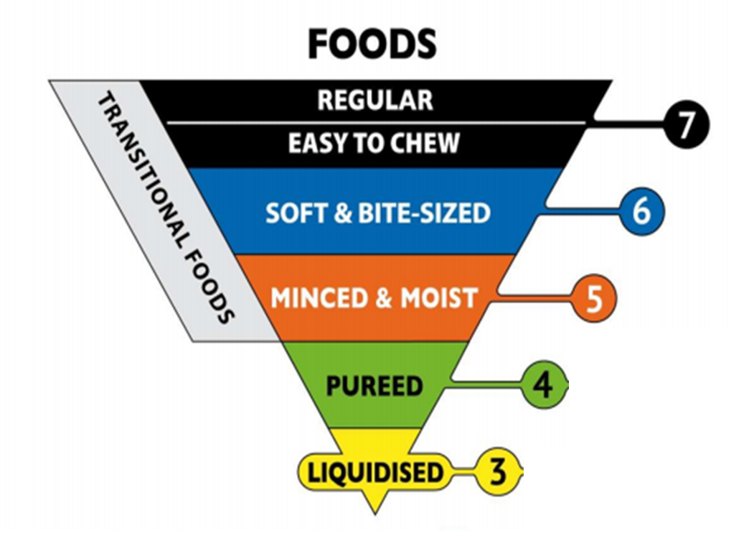
Following assessment, a speech pathologist will recommend the food consistency that is safest and easiest for an individual to swallow. The entire meal must meet the recommended texture, not just part of the meal.
IDDSI Description/ Characteristics:
- Usually eaten with a spoon (a fork is possible)
- Cannot be drunk from a cup because it does not flow easily
- Cannot be sucked through a straw
- Does not require chewing
- Can be piped, layered or molded because it retains its shape, but should not require chewing if presented in this form
- Shows some very slow movement under gravity but cannot be poured
- Falls off spoon in a single spoonful when tilted and continues to hold shape on a plate • No lumps
- Not sticky
- Liquid must not separate from solid

